Baldness is a common concern for many individuals, especially as they age. It can have a significant impact on self-esteem and overall confidence. Understanding the stages of baldness is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different stages of baldness, from the early signs to more advanced patterns. We will also discuss various treatment options and tips for maintaining healthy hair. Whether you are experiencing hair loss or want to learn more about this topic, this guide will provide valuable insights and information.
The Norwood Scale: A Tool for Classification
What is the Norwood Scale?
The Norwood Scale, also known as the Hamilton-Norwood scale, is widely used to measure the extent of male pattern baldness. Developed by Dr O’Tar Norwood in the 1970s, it provides clinicians with a standardized way to assess the severity and pattern of hair loss in men.
How Does the Norwood Scale Work?
The Norwood Scale consists of seven stages that indicate different degrees of baldness. Each step represents a specific pattern of hair loss, ranging from minimal to extensive. By using this scale, doctors can diagnose the extent of baldness, discuss treatment options, and track the effectiveness of treatment over time.
The 7 Stages of Baldness
Understanding the seven stages of baldness according to the Norwood Scale is essential for recognizing and assessing the progression of hair loss. Let’s explore each stage in detail:
Stage 1: No Significant Hair Loss
In stage 1, individuals have a full head of hair with no signs of baldness or a receding hairline. There is no noticeable hair loss at this stage, and the hairline remains intact.
Stage 2: Slight Recession of the Hairline
During Stage 2 of hair loss, individuals may observe a gradual recession of the hairline around the temples, often labelled as an adult or mature hairline. Such changes are typically insignificant and do not warrant any immediate concern.
Stage 3: Signs of Clinically Significant Balding
Stage 3 marks the first signs of clinically significant balding. The hairline starts to recede deeply at both temples, forming an M, U, or V shape. The areas of recession may be completely bare or sparsely covered with hair. This stage is often where individuals become aware of their hair loss.
Stage 3 Vertex: Hair Loss on the Top of the Scalp
Stage 3 vertex is a variation of stage 3 where the hairline remains at stage 2. However, there is significant hair loss on the top of the scalp (the vertex). This results in a more pronounced thinning or bald spot on the crown of the head.
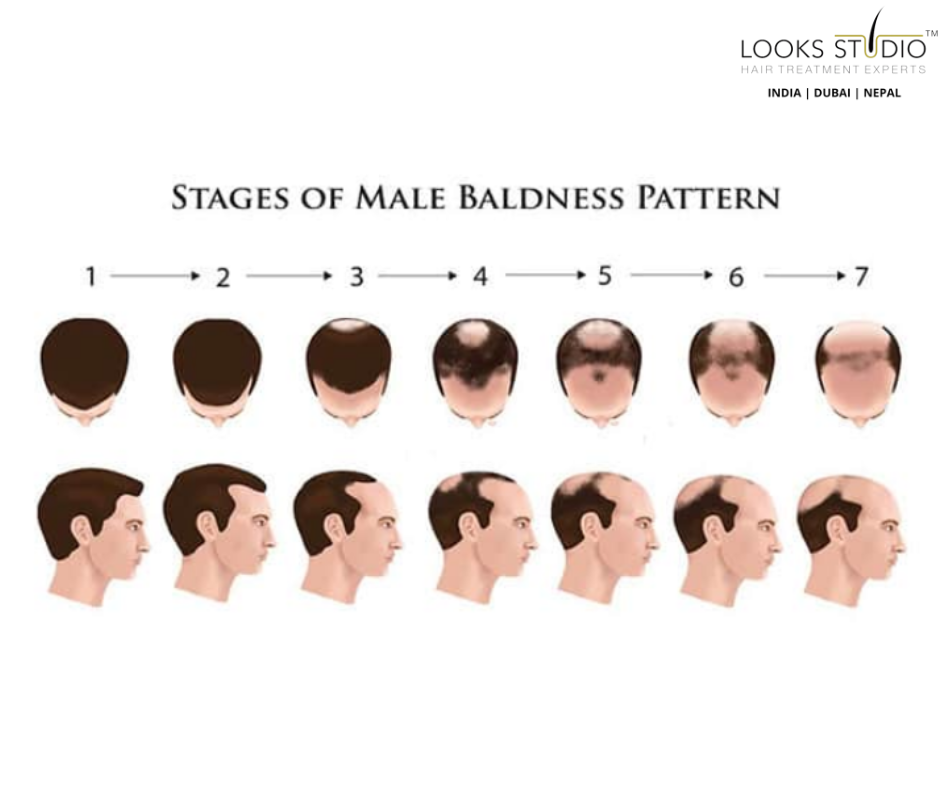
Stage 4: Severe Hairline Recession
In stage 4 of hair loss, the hairline recession becomes more severe than in stage 2. The vertex may display sparse hair or be completely bald, while the areas of hair loss are divided by a strip of hair that links to the hair still present on the sides of the scalp. As a result, the hairline takes on a more pronounced U-shape.
Stage 5: Larger Areas of Hair Loss
As the hair loss advances to stage 5, the impacted areas substantially increase in size compared to stage 4. Despite the balding areas remaining separate, the hair strip between them narrows and thins out. Consequently, the pattern of hair loss assumes a more distinct horseshoe form.
Stage 6: Balding Areas Joining Together
Stage 6 is characterized by the joining of the balding areas at the temples with the balding area at the vertex. The band of hair across the top of the head becomes less dense or sparse, creating a more pronounced horseshoe-shaped pattern.
Stage 7: Most Severe Stage of Hair Loss
Stage 7 represents the most severe stage of hair loss. Only a band of hair going around the sides of the head remains, and this hair is usually thin and fine. The balding areas on the top of the head and the sides merge, resulting in extensive hair loss.
Norwood Class A: A Different Progression
Apart from the common seven stages of male pattern baldness, there exists a rarer variation known as Norwood Class A. This variation is characterized by a symmetrical receding hairline without leaving a tuft of hair in the center, and there is no bald spot on the crown. Instead, the hairline moves directly from the front to the back.
What Causes Male Pattern Hair Loss?
Understanding the underlying causes of male pattern hair loss is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies. While the exact cause is not fully understood, it is believed to be a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors.
Genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors all play a role in male pattern hair loss. Genetic factors inherited from both parents determine an individual’s sensitivity to androgens, especially dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which regulates hair growth cycles.
Each hair strand undergoes a growth phase, a resting phase, and then falls out to be replaced by new hair. Increased androgens in the hair follicles can lead to shorter growth cycles, resulting in thinner and shorter hairs. Over time, the hair follicles become smaller and less capable of producing new hairs, ultimately leading to hair loss.
While environmental factors such as stress, poor nutrition, and certain medications may also contribute to hair loss, they usually have a secondary impact compared to genetic and hormonal factors.
Diagnosing Male Pattern Baldness
Male pattern baldness can be identified through a physical examination and detailed medical history. The distinct pattern and distribution of hair loss in most cases signal male pattern baldness. However, in some cases, it may be necessary to eliminate other potential causes, especially in young individuals or those experiencing unusual hair loss patterns.
During the physical exam, a dermatologist or hair loss specialist will scrutinize the scalp to assess the pattern and extent of hair loss. They may also conduct a gentle tug test to evaluate the strength and quality of the hair follicles.
To identify any underlying medical conditions, medications, or lifestyle factors that may contribute to hair loss, a comprehensive medical history will be taken. This information will help determine the most suitable treatment options and exclude any other potential causes of hair loss.
Treatment Options for Hair Loss
Treating hair loss is most effective when started early. It is easier to slow down hair loss than it is to stimulate new hair growth once significant hair loss has occurred. Various treatment options are available, ranging from over-the-counter treatments to prescription medications and medical procedures.
Over-the-counter (OTC) Treatments
Over-the-counter treatments are accessible options for individuals experiencing early-stage hair loss. These treatments include:
Minoxidil (Rogaine): Minoxidil is a topical medication that can be directly applied to the scalp. It helps prevent hair thinning and stimulates hair growth on the top of the scalp. Minoxidil can be used in combination with other treatments for enhanced results.
Laser Devices: There are various laser devices available, such as brushes and combs, that emit laser light to stimulate hair growth. While their effectiveness is not clinically proven, some individuals may find them beneficial.
Prescription Treatments
For individuals with more advanced hair loss or those who do not respond well to over-the-counter treatments, prescription medications may be recommended. The most common prescription medication for male pattern baldness is finasteride (Proscar, Propecia).
Finasteride: Finasteride is an oral medication approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of male pattern hair loss. It works by blocking the conversion of testosterone to DHT, thereby reducing the levels of DHT in the scalp. Finasteride has been shown to slow down hair loss in approximately 88% of men and stimulate hair regrowth in about 66% of men.
Medical Procedures
For individuals with more advanced hair loss or those who desire more significant improvements, various medical procedures may be considered.
Surgical Procedure
Hair Transplantation: Hair transplantation involves removing healthy hair follicles from areas of good hair growth (donor sites) and transplanting them into balding areas (recipient sites). This procedure allows for the restoration of hair growth in areas of significant hair loss.
It is essential to consult with a qualified hair transplant expert, such as Looks Studio, to determine the most suitable treatment option based on individual needs and goals. With over 10 years of experience in hair transplant procedures, Looks Studio offers expert guidance and personalized solutions for hair loss.
Coping with Hair Loss
Coming to terms with hair loss and finding ways to cope with it is an important aspect of the journey. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach, here are some strategies individuals can consider:
Accepting Baldness as a Natural Part of Aging
Recognizing that baldness is a natural part of the ageing process can help reduce feelings of embarrassment or shame associated with hair loss. Embracing one’s appearance and focusing on other aspects of personal and physical well-being can contribute to a positive outlook.
Choosing Treatment Options
Deciding on the most suitable treatment option depends on individual preferences, goals, and the extent of hair loss. Some individuals may prefer to pursue medical procedures such as hair transplantation, while others may opt for non-surgical options like scalp micropigmentation or simply embrace their baldness without intervention
Shaving the Head as an Alternative
For individuals who prefer a clean-shaven look, shaving the head entirely can be a liberating choice. This eliminates the need for ongoing maintenance and can provide a sense of empowerment and confidence.
It is important to remember that baldness does not define one’s worth or attractiveness. Everyone has their unique journey, and embracing oneself fully, with or without hair, is a powerful statement of self-acceptance.
Conclusion
It is crucial for people who experience hair loss and want to find the right treatment to understand the stages of baldness. The Norwood Scale is a standardized classification system that evaluates the pattern and severity of male pattern baldness. By recognizing the signs and stages of hair loss, individuals can seek advice from healthcare professionals, evaluate different treatment options, and make informed decisions about their hair health.
There are many options available to address hair loss, including over-the-counter treatments like minoxidil and laser therapy, prescription medications like finasteride, and medical procedures such as hair transplantation. Additionally, adopting healthy lifestyle habits and coping strategies can contribute to overall hair health and personal well-being.
It’s important to remember that hair loss is a natural process that affects many individuals, and there is no right or wrong way to approach it. It’s essential to embrace your unique journey and remember that confidence and self-acceptance are the most beautiful qualities one can possess, with or without hair.


 . Now
. Now